What is IGBT
IGBT stands for Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor. It is a type of semiconductor device used in various applications, especially in power electronics and high-power systems. IGBTs combine the characteristics of both MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) and bipolar transistors, making them suitable for switching high voltages and currents.
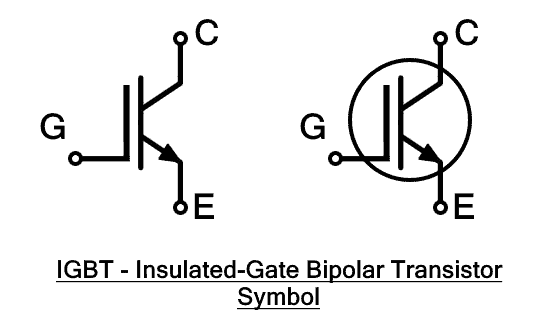
Features and characteristics of IGBTs
- Voltage and Current Handling: IGBTs are designed to handle high voltage and current levels, making them suitable for applications where power amplification or switching is required.
- Voltage-Controlled and Current-Carrying: IGBTs have a voltage-controlled gate, similar to MOSFETs, which makes them easy to drive and control. However, they are capable of carrying high currents like bipolar transistors.
- Fast Switching Speed: IGBTs can switch on and off relatively quickly, which is essential for applications like motor control, inverters, and power converters.
- High Input Impedance: They have a high input impedance, meaning they require minimal current to control the switching operation.
- Insulated Gate: The gate of an IGBT is electrically insulated from the main current-carrying terminals. This isolation helps protect the control circuitry from the high voltage in the power circuit.
IGBTs applications
- Motor Drives: IGBTs are used in variable frequency drives (VFDs) to control the speed of electric motors efficiently.
- Inverters: They are used in inverters to convert DC power to AC power, which is essential in applications like renewable energy systems (e.g., solar and wind inverters) and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
- Induction Heating: IGBTs are used in high-frequency induction heating applications, such as metal hardening and cooking appliances.
- Welding Equipment: They are employed in welding machines for precise control of the welding process.
- Power Supplies: IGBTs can be found in high-power switch-mode power supplies for various industrial and electronic applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of IGBT
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) offer several advantages and have some disadvantages, depending on the specific application and requirements. Here are the main advantages and disadvantages of IGBTs:
Advantages:
- High Voltage and Current Handling: IGBTs can handle high voltage and current levels, making them suitable for high-power applications.
- Fast Switching Speed: They have relatively fast switching speeds, allowing for efficient control of power electronics systems.
- Voltage-Controlled: IGBTs are voltage-controlled devices, which means they are easy to drive and control using low-power gate signals.
- Low Conduction Loss: IGBTs have lower conduction losses compared to traditional bipolar transistors, making them more energy-efficient for high-power applications.
- High Input Impedance: They have a high input impedance, requiring minimal current to control the gate, reducing the drive circuit’s power requirements.
- Reliability: IGBTs are known for their high reliability and robustness, making them suitable for critical applications.
- Isolated Gate: The gate of an IGBT is electrically isolated from the main power terminals, providing added safety and protection to the control circuitry.
Disadvantages:
- Switching Losses: IGBTs can have relatively high switching losses, especially when compared to MOSFETs. This can result in some energy dissipation during switching, affecting overall efficiency.
- Limited Frequency Range: IGBTs may not be suitable for very high-frequency applications due to their inherent switching limitations. In such cases, MOSFETs or other devices might be preferred.
- Temperature Sensitivity: IGBTs can be sensitive to temperature variations, and their performance may degrade at high temperatures. Adequate cooling and thermal management are essential for reliable operation.
- Complex Drive Circuitry: While IGBTs are voltage-controlled, their drive circuitry can be more complex than that of MOSFETs, especially in high-power applications.
- Higher Cost: IGBTs can be more expensive than some other semiconductor devices, such as MOSFETs, which can be a factor in cost-sensitive applications.
- Limited Voltage Rating: IGBTs may not be suitable for extremely high-voltage applications, as other devices like silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFETs or thyristors might offer better performance in such cases.
- Parasitic Components: IGBTs have inherent parasitic capacitances and inductances that can affect their performance at high frequencies and require careful consideration in circuit design.
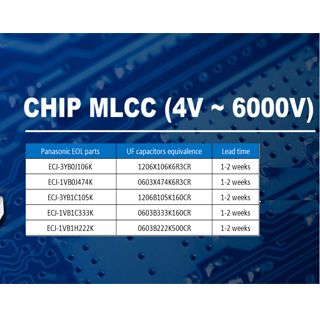
To replace brands Infineon, Onsemi, ST, Diodes, Vishay
IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) is a semiconductor device that combines the advantages of MOSFET and bipolar transistor technologies.
It is widely used in high-power applications where efficient switching and control of high voltages and currents are crucial.
The IGBT operates as a voltage-controlled bipolar transistor with an insulated gate, allowing for precise and fast switching.
Topdiode already supply their IGBT to automotive electronics, solar energy, power market, 5G telecommunication. Industrial and consumer electronics. To replace brands Infineon, Onsemi, ST, Diodes, Vishay etc .
| Topdiode PN | Package | Pin to Pin replacement | ||
| Brands | P/N# | Package | ||
| TJT020N065FED-F-BR | TO-220MF | AOS | AOTF20B65M1 | TO-220 |
| TJT030N065FED-F-BR | TO-220F | ST | STGP30NC60K | TO-220 |
| TJT040K065WED-GE-BR | TO-247 | ST | STGWA40H65DHFB2 | TO-247 |
| TJNG15T60FS | TO-220F | KEC | KGF12N60FDA | TO-220IS |
| TXNS20N60T | TO-247 | On semi | FGH20N60SFD | TO-247-3LD |
| TXNS40N60T | TO-247 | On semi | FGH40N60SFD | TO-247-3LD |
| TXNS40N120TB | TO-247 | On semi | FGH40T120SMD | TO-247-3LD |
| TNCE30TD60B | TO-220 | ST | STGP30V60DF | TO-220 |
| TNCE40TD60BT | TO-247 | Infineon | IKW40N60H3 | PG-TO247-3 |
| TNCE60TD60BT | TO-247 | AOS | AOK60B60D1 | TO-247 |
| TNCE60TD65BT | TO-247 | AOS | AOK60B65H2AL | TO-247 |
| TNCE80TD60BT | TO-247 | ST | STGW80V60DF | TO-247 |
| TNCE80TD65BT | TO-247 | ST | STGW80H65DFB-4 | TO-247-4 |
| TNCE40TD120WW | TO-264 | On semi | FGL40N120ANDTU | TO-264 |