tantalum capacitor
Tantalum capacitors are a type of electrolytic capacitor known for their compact size, high capacitance, and reliability.
Tantalum Capacitor
Tantalum capacitors are a type of electrolytic capacitor that uses tantalum metal as one of the electrodes.
Tantalum capacitors are a type of electrolytic capacitor known for their compact size, high capacitance, and reliability. They use tantalum metal as the anode (positive electrode), and the dielectric material is typically a thin oxide layer formed on the surface of the tantalum metal.
Tantalum Capacitor Description
Tantalum capacitors are a type of electronic component used in electronic circuits for energy storage and filtering.
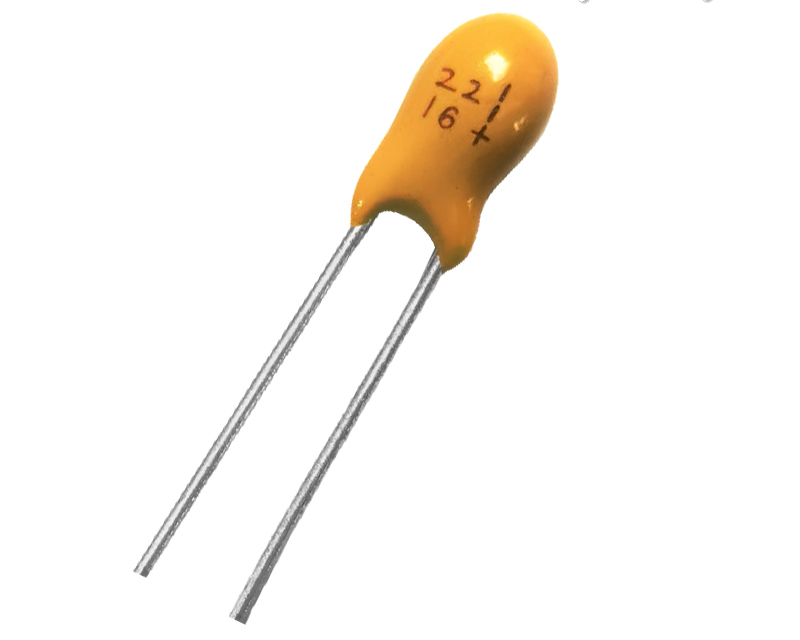

Tantalum Capacitors - Solid Leaded 4.7uF 50V +/-20%
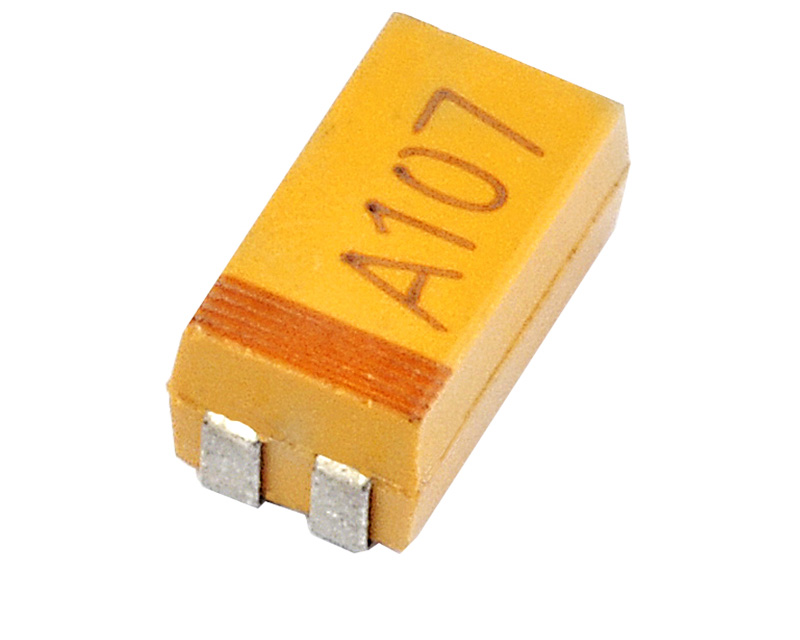
Chip Tantalum Capacitors 68uF 16V +/-10% Case D
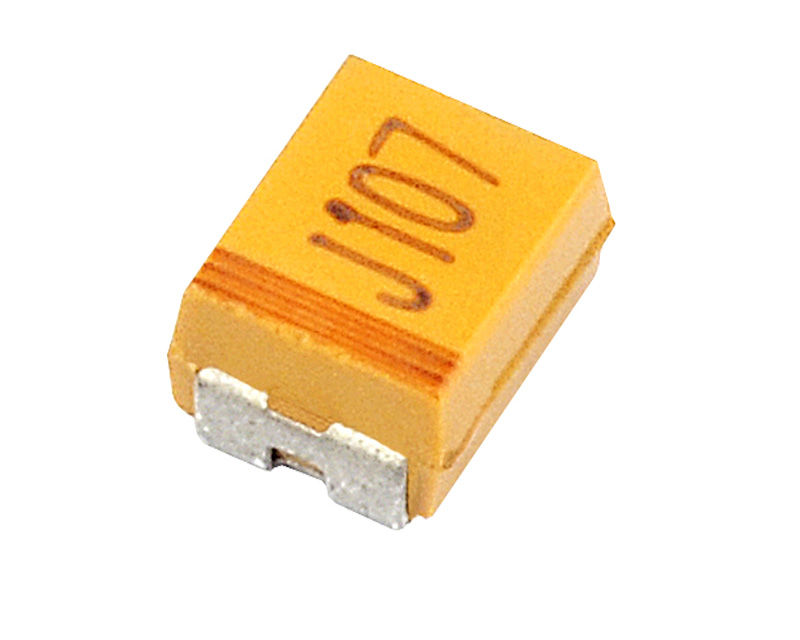
CA45U Low ESR Tantalum Chip Capacitor
Tantalum capacitors
Tantalum capacitors are usually polarized, meaning that they have a positive and negative side. It is important to ensure the correct polarity is used when installing them; otherwise, the capacitor could be damaged. This is done by connecting the positive side of the capacitor to the positive side of the circuit and the negative side of the capacitor to the negative side of the circuit.
- High capacitance per volume ratio: Tantalum capacitors have a high capacitance per volume ratio, which means they can store a large amount of charge in a relatively small size. This makes them suitable for use in applications where size is a critical factor.
- Long lifespan: Tantalum capacitors have a long lifespan compared to other types of capacitors. They can last up to 50 years, making them a popular choice for use in electronic devices.
- High stability and reliability: Tantalum capacitors are known for their high stability and reliability. They are less likely to fail or change their capacitance value over time.
- Low leakage current: Tantalum capacitors have a low leakage current, which means they can maintain their charge for a longer period of time.
- Suitable for use in high temperature environments: Tantalum capacitors are suitable for use in high temperature environments, which makes them ideal for use in industrial and automotive applications.
- High cost compared to other capacitors: Tantalum capacitors are more expensive compared to other types of capacitors. This may make them less attractive for use in cost-sensitive applications.
- Sensitivity to voltage spikes and transients: Tantalum capacitors are sensitive to voltage spikes and transients, which can cause them to fail if they are exposed to excessive voltage or current.
- Risk of thermal runaway and catastrophic failure: When subjected to excessive voltage or current, tantalum capacitors can experience thermal runaway, which can lead to catastrophic failure.
- Piezoelectric effects: Some types of tantalum capacitors may exhibit piezoelectric effects, which can cause noise or distortion in audio applications.
Tantalum capacitors are used in a wide range of applications due to their high capacitance, low ESR (equivalent series resistance), and low-cost per unit. They are used in a variety of industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, aerospace, medical, and industrial.
In consumer electronics, tantalum capacitors are used to reduce noise, filter power, and increase the life of the circuit. They are used in power supplies, audio amplifiers, and other power-sensitive applications.
In automotive applications, tantalum capacitors are used to reduce noise and improve the overall efficiency of the vehicle. They are used in powertrain control systems, engine management, and traction control.
In aerospace applications, tantalum capacitors provide reliable and efficient power delivery to systems that require precision control. They are used in navigation systems, flight control systems, and other critical components.
In medical applications, tantalum capacitors are used to improve patient safety by providing reliable power delivery. They are used in pacemakers, defibrillators, and other vital medical devices.
In industrial applications, tantalum capacitors are used for power conditioning, voltage regulation, and power monitoring. They are used in motor control systems, process control systems, and other industrial applications.
Overall, tantalum capacitors are a versatile component that is used in many different applications due to their high capacitance, low ESR, and low cost per unit. They can be used to reduce noise, filter power, improve efficiency, and provide reliable power delivery.
Topdiode services are designed to meet the needs of customers seeking cost savings with faster project timelines, please contact info@topdiode.com for more information.
Topdiode Group Factory
Tantalum Capacitors FAQs
Identifying tantalum capacitors involves examining their physical appearance and, in some cases, checking for markings or color codes. Here are some steps to help you identify tantalum capacitors:
Color and Shape:
- Tantalum capacitors are often smaller and more compact than other types of electrolytic capacitors. They typically have a distinctive molded, rectangular shape.
- The color of the casing can vary, but it's commonly a darker color, such as dark gray, black, or dark blue.
Markings:
- Tantalum capacitors may have markings or labels that indicate their capacitance, voltage rating, and tolerance. These markings are often alphanumeric codes.
- Look for any stamped or printed text on the capacitor. The markings may be on one or both ends of the capacitor or on its body.
Polarity:
- Tantalum capacitors are polarized, meaning they have a positive and a negative lead. The positive lead is typically longer and may have a “+” sign or a colored band.
- Be sure to observe the polarity marking, and ensure that you connect the capacitor correctly in the circuit to prevent damage.
Size:
- Tantalum capacitors are generally smaller than aluminum electrolytic capacitors with similar capacitance values.
- Compare the size of the capacitor with other capacitors in the circuit. Tantalum capacitors are often chosen when space is a critical factor.
Color Coding:
- Some tantalum capacitors have color-coding bands to indicate their values. These bands are similar to the color codes used on resistors.
- Refer to the datasheet or a reference guide to interpret the color codes correctly.
Datasheet:
- If available, refer to the datasheet for the capacitor. The datasheet provides detailed information about the capacitor's specifications, including capacitance, voltage rating, and other technical details.
Always exercise caution when handling electronic components, and be aware that misidentification or mishandling can lead to damage. If you're uncertain about the identification of a capacitor, consult the manufacturer's documentation or seek guidance from experienced individuals in the electronics field.
While tantalum capacitors and electrolytic capacitors are both types of electrolytic capacitors, they have some differences that should be considered before replacing one with the other. Here are some factors to keep in mind:
Polarity:
- Tantalum capacitors are polarized, meaning they have a positive and a negative lead, and must be connected in the correct orientation in the circuit.
- Electrolytic capacitors, including tantalum, are also polarized. Ensure that the replacement electrolytic capacitor has the correct polarity and is connected in the same way.
Size and Form Factor:
- Tantalum capacitors are generally smaller and more compact than aluminum electrolytic capacitors for similar capacitance values.
- Check the physical size of the replacement capacitor to ensure it fits in the designated space on the circuit board.
Capacitance and Voltage Rating:
- Ensure that the replacement capacitor has the same or higher capacitance and voltage rating as the original tantalum capacitor.
- Exceeding the voltage rating of the original capacitor could lead to failure or damage.
Application Considerations:
- Tantalum capacitors are often chosen for applications where space is a critical factor due to their high volumetric efficiency.
- If space is not a concern, you may use an aluminum electrolytic capacitor as a replacement, but it's essential to consider the specific requirements of the circuit.
Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR):
- Tantalum capacitors generally have lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors. In some circuits, especially those with high-frequency components, this difference might be critical.
Before replacing a tantalum capacitor with an electrolytic capacitor, it's recommended to consult the circuit's design, refer to the component datasheets, and consider the factors mentioned above. If possible, follow the manufacturer's recommendations and guidelines for capacitor replacements. Additionally, in critical applications, it's advisable to seek the advice of an electronics professional or engineer.
Yes, tantalum capacitors are polarized components. This means they have a specific orientation in which they must be connected within an electronic circuit. Tantalum capacitors have a positive (+) and a negative (-) lead, and it's crucial to connect them correctly to avoid malfunction or damage.
The positive lead is typically longer, and the negative lead may be marked with a stripe, a minus sign (-), or some other indicator. It's important to pay attention to the polarity markings on the capacitor and ensure that it is installed in the circuit with the correct orientation.
Incorrectly connecting a tantalum capacitor in reverse polarity can lead to overheating, leakage, or even catastrophic failure, as the dielectric oxide layer on the tantalum surface is sensitive to reverse voltage. Always follow the manufacturer's recommendations and the circuit design specifications when working with polarized components.
Checking a tantalum capacitor with a multimeter involves measuring its capacitance, checking for proper polarity, and examining for any signs of a short circuit or leakage. Here's a step-by-step guide:
1. Check Polarity:
- Identify the positive (+) and negative (-) leads on the tantalum capacitor. The positive lead is typically longer and may be marked with a stripe, a plus sign (+), or other indicators.
- Set your multimeter to the continuity or diode check mode.
- Place the multimeter probes on the capacitor leads. If the multimeter beeps or shows continuity, it indicates the correct polarity. If there's no continuity, reverse the probe connections; if it beeps or shows continuity, the capacitor is reversed.
2. Check Capacitance:
- Set your multimeter to the capacitance measurement mode. Choose a range that is higher than the expected capacitance value of the tantalum capacitor.
- Connect the multimeter probes to the capacitor leads, observing proper polarity.
- The multimeter should display the capacitance value. Compare this value to the specified capacitance on the capacitor or its datasheet. Tantalum capacitors are polarized, so the measured capacitance should match the specified value closely.
3. Check for Shorts:
- Set the multimeter to the resistance (ohms) mode.
- Connect one probe to the positive lead of the capacitor and the other to the negative lead.
- The resistance should initially be high and then gradually decrease as the capacitor charges. If the resistance remains very low or shows continuity, it may indicate a short circuit, and the capacitor may be faulty.
4. Check for Leakage:
- Set the multimeter to a high resistance range (ohms).
- Connect one probe to the positive lead of the capacitor and the other to the negative lead.
- The resistance should start high and gradually decrease as the capacitor charges. If the resistance remains very high, it may indicate leakage, and the capacitor may be faulty.
